OSR论文阅读1
Published:
这篇博客介绍了我在阅读一系列有关于开集识别的论文时的笔记
Paper1-Learning multiple gaussian prototypes for open-set recognition
发表杂志:一区Information Sciences
作者:Jiaming Liu, Jun Tian, Wei Han,Zhili Qin,Yulu Fan,Junming Sha
单位:成电
摘要
开集识别的目的是处理在训练阶段不存在的未知类,其关键点是学习有效的潜在特征表示来对已知的类别进行分类以及检测新出现的类别。在本文中,我们学习了多个高斯原型,以生成和判别两种方式更好地表示复杂的类分布。通过生成约束,同一类的潜在变量紧密地聚集在相应的高斯原型周围,为未知类的样本保留了额外的空间。判别约束将不同类别的高斯原型分离开来,进一步提高了对已知类别的判别能力。重要的是,整个框架可以直接从贝叶斯推理中推导出来,从而为开集识别提供了理论支持。不同数据集的实验结果验证了该方法的可靠性和有效性。代码在:https://github.com/LiuJMzzZ/MGPL
方法详解
开集识别类似于Novelty Detection异常检测任务,也即都是从正常的样本中检测出离群的样本。
- 最著名的一个原型学习的例子是KNN
paper2-DGSSC: A Deep Generative Spectral-Spatial Classifier for Imbalanced Hyperspectral Imagery
DGSSC包括三个组件,一个两阶段编码器,一个解码器和一个分类器; 编码器的第一阶段包括连续的三维(3D)和二维(2D)卷积,探索频谱空间和深度空间信息。 第二阶段涉及深度潜变量模型,以实现少数类数据的增强。
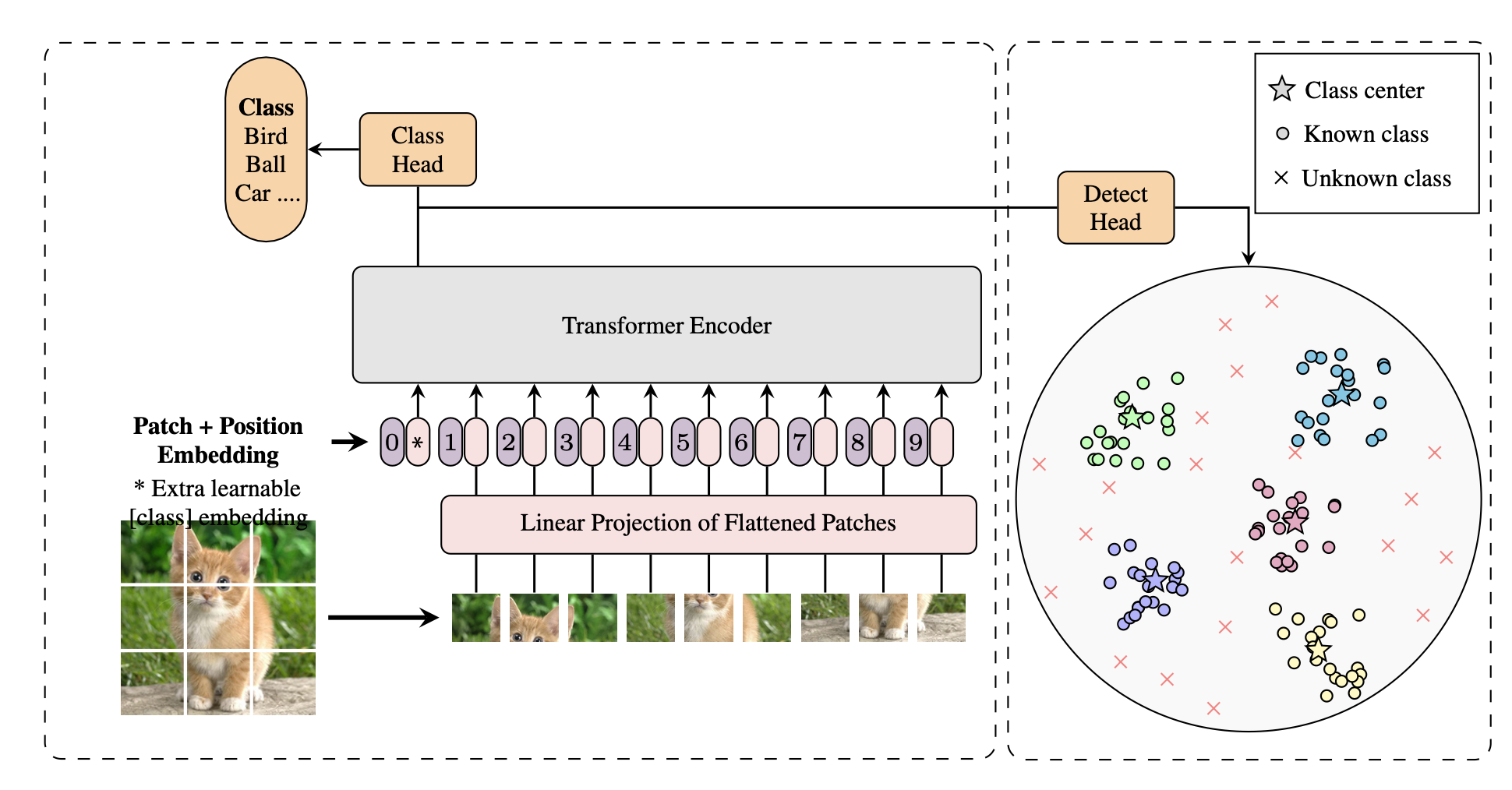
paper3: Open Set Recognition using Vision Transformer with an Additional Detection Head
摘要
Deep neural networks have demonstrated prominent capacities for image clas- sification tasks in a closed set setting, where the test data come from the same distribution as the training data. However, in a more realistic open set scenario, traditional classifiers with incomplete knowledge cannot tackle test data that are not from the training classes. Open set recognition (OSR) aims to address this problem by both identifying unknown classes and distinguishing known classes simultaneously. In this paper, we propose a novel approach to OSR that is based on the vision transformer (ViT) technique. Specifically, our approach employs two separate training stages. First, a ViT model is trained to perform closed set classification. Then, an additional detection head is attached to the embed- ded features extracted by the ViT, trained to force the representations of known data to class-specific clusters compactly. Test examples are identified as known or unknown based on their distance to the cluster centers. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time to leverage ViT for the purpose of OSR, and our extensive evaluation against several OSR benchmark datasets reveals that our approach significantly outperforms other baseline methods and obtains new state- of-the-art performance.